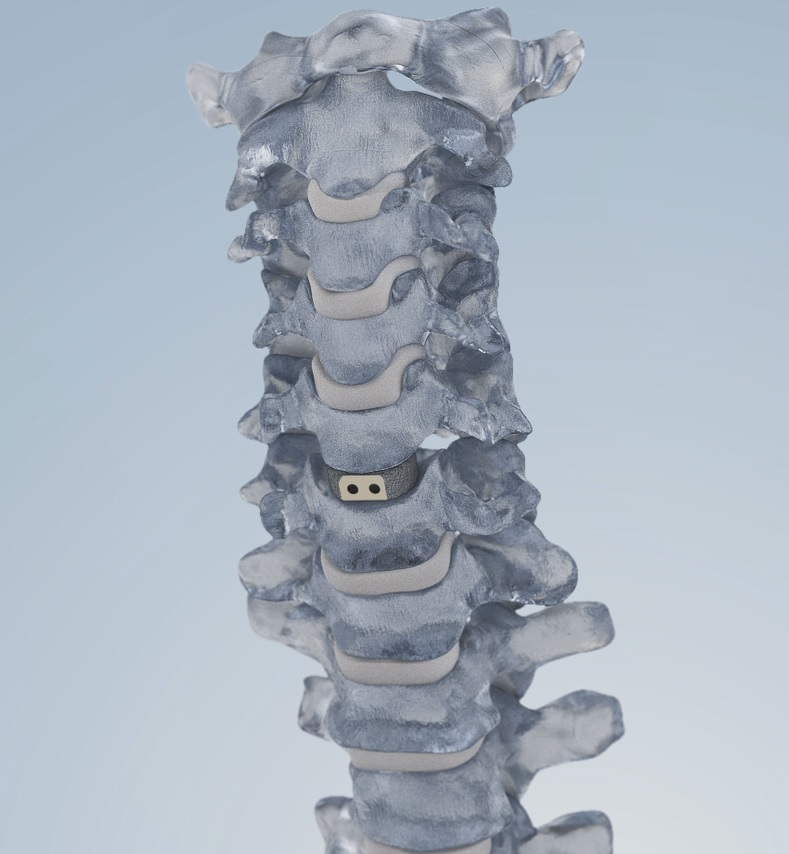
Spinal Endoscopy
Spinal endoscopy is a cutting-edge, minimally invasive surgical technique used to diagnose and treat various spinal conditions. This procedure involves the use of an endoscope—a thin, flexible tube equipped with a camera and light source—to visualize and access the spinal canal and surrounding structures. Spinal endoscopy has gained popularity in recent years due to its precision, reduced recovery time, and lower risk of complications compared to traditional open spinal surgery.
Tubular Retractors
Minimally invasive spinal surgery (MISS) using tubular retractors is a advanced surgical technique designed to treat various spinal conditions with minimal disruption to surrounding tissues. This approach involves the use of small, cylindrical tubes (tubular retractors) to create a pathway to the spine, allowing surgeons to access the affected area while minimizing damage to muscles and soft tissues. This method has become increasingly popular due to its precision, reduced recovery time, and lower risk of complications compared to traditional open spinal surgery.
Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion (TLIF)
Minimally Invasive Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion (TLIF) is an advanced surgical technique used to treat spinal instability, degenerative disc disease, spondylolisthesis, and other conditions affecting the lumbar spine. This procedure involves fusing two or more vertebrae together to stabilize the spine while using a minimally invasive approach to reduce tissue damage and promote faster recovery. Here is an overview of the risks, benefits, and potential complications associated with minimally invasive TLIF.
Spinal Fixation Using MIS Technology
Minimally Invasive Spinal (MIS) fixation is a modern surgical technique used to stabilize the spine in cases of spinal instability, fractures, degenerative conditions, or deformities. This approach utilizes advanced MIS technology, such as specialized instruments, imaging guidance, and percutaneous screw systems, to perform spinal fixation with minimal disruption to surrounding tissues. MIS fixation has become increasingly popular due to its precision, reduced recovery time, and lower risk of complications compared to traditional open spinal surgery.