Useful links
Different types of fractures may affect the spine; some are simple and can be treated with external immobilisation like Miami J collar or Halo immobilisation. Other fracture may need urgent surgical intervention for two reasons
– If the fracture affects the spinal mechanical stability, high risk of injury to the adjacent neural tissue.
-If the fracture is already displaced the bone, causing neural tissue compression or damage, like spinal cord or the nerve roots which may lead to pain or neurological deficit correlate to the affect area of the spine. In this case, neural tissue decompression and spinal column fixation is the target.
Surgical procedures for spinal fractures are very complex and variable. Most of the cases are done on emergency situation or an expedited manner; however, initial conservative treatment may be indicated at the beginning to avoid the surgery.
Before
After
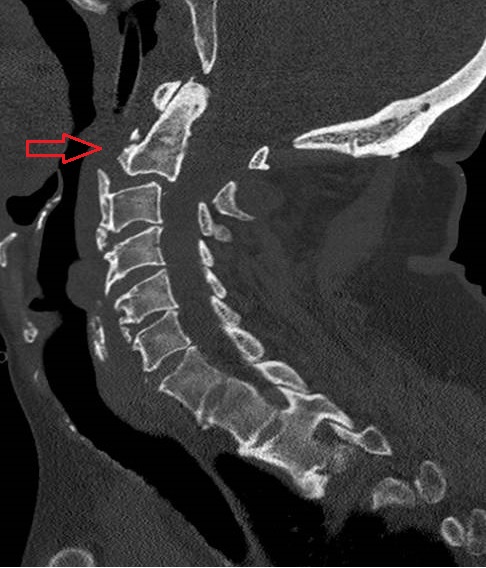
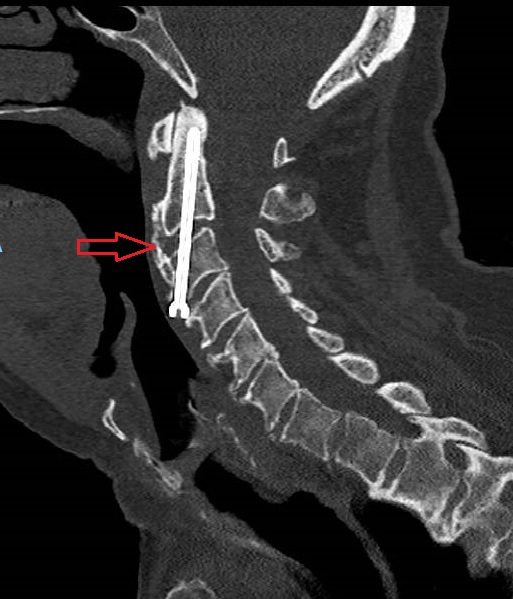
Spinal fractures can be classified in to 2 types
Pathological spinal fractures: The most common cause of pathological spinal fractures is osteoporosis, weak and brittle bone disease affecting old age population, women are mostly affected by this disease.
Metastatic spinal tumours are also common cause of pathological fractures. Other conditions like Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal hyperostosis or Ankylosing spondylitis which may lead to very unstable fractures of the spine
The fractures of the bone happens with very trivial trauma, sometime with no trauma. The symptoms are vary from mild back pain and numbness of the arms and legs to complete paralysis of the limbs, sphincters and different sensory changes. It depends on the type, level and severity of the fractures and underlying disease process.
Traumatic Spinal fractures: very common in instance of trauma, may affect different parts of spine.
Diagnosis: CT and MRI scans are the ideal investigation for spinal fractures. However, X-rays may play a role in assessment of the stability of the spine in certain situation like standing X-rays to assess the spinal alignment, flexion/extension radio graphs to assess the stability of the mobile part of the spine at Cervical and lumbar areas.
Treatment:
There are few options of treatment of spinal fractures
-Conservative treatment: without any immobilisation of the affected part of the spine. mostly indicated in radiologically stable spinal fractures. most of the time, fractures will heal without any intervention in 8-12 weeks. Good analgesia is necessary to help the patients in coping with back pain. small percentage of patient with such fractures may develop worsening of the symptoms, they need to seek urgent medical attention for further evaluation and treatment.
-External Immobilistaion(EI): In certain types of spinal fractures, or medically unfit patients for surgery, an external immobilisation is an option to support the spine without surgery. Different types of EI available for different areas of the spine. The surgeon and physiotherapist are usually decide on the best option for the patient, with consideration of each patient’s need.
-Internal Spinal fixation: This include insertion of metal implants to stabilise the spinal column. Most of the cases are permanently inserted , however, removal of the implants may be considered in certain situation.
